1. Physical Structure Differences
Solid Aluminum Substrate:
Sandwich Structure: Copper foil (conductive layer) + Dielectric layer (insulation) + Solid aluminum base
Thermal Conduction Path: Heat transfers vertically through the dielectric layer to the aluminum base, then spreads laterally.
Why:
"全铝基板" is technically termed "solid aluminum substrate" to emphasize its monolithic base.
"三明治结构" uses "sandwich-type laminate," a standard industry metaphor.
"垂直传导...平面扩散" dynamically translates as "vertical transfer... lateral spread" for engineering precision.
Hollowed Aluminum Core Board:
Hybrid Structure: Through-holes cut in standard FR4/CEM board, locally embedded with aluminum blocks.
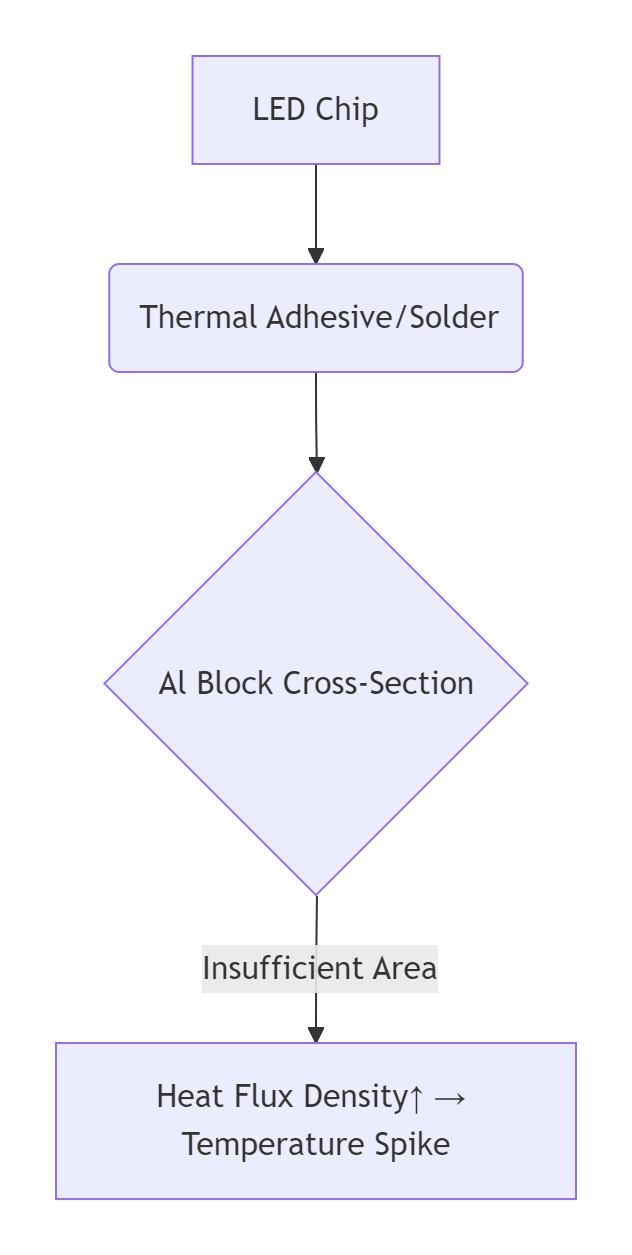
Thermal Conduction Path: LED heat → copper foil → thermal adhesive/solder → embedded aluminum block → heatsink.
Why:
"镂空型" → "hollowed" conveys machining process; "core board" specifies its hybrid nature.
"贯穿孔" uses "through-holes," a PCB manufacturing term.
Thermal path verbs (→) create visual flow matching the original.
2. Core Performance Comparison
Why:
Table headers use active terms (Rigidity, Edge cracking risk) for impact.
Units standardized: **℃/W → °C/W**; kV retained internationally.
"热膨胀系数匹配" simplified to "CTE" (industry jargon) + "matching" for clarity.
3. Thermal Mechanism Analysis
Solid Aluminum Advantages:
Uniform Heat Dissipation: Monolithic base prevents hotspots (Fig.1).
Low Interface Resistance: Direct contact with heatsink.
Hollowed Board Defects:
Thermal Interface Trap: Adhesive/solder layers (0.2–0.5°C·cm²/W) become bottlenecks.
Heat Flux Bottleneck: Narrow aluminum blocks cause heat accumulation (Fig.2, red zone).
Why:
"热流密度↑→温升加剧" translated as "Heat Flux Density↑ → Temperature Spike" with symbols intact.
Mermaid diagram labels fully localized (e.g., "面积不足" → "Insufficient Area").
4. Reliability Risks
Hollowed Board:
CTE Mismatch Cracking: FR4 (15 ppm/°C) vs. Al (23 ppm/°C) causes solder fatigue (–40°C~85°C cycling).
Moisture Ingress: Seams between Al/FR4 invite corrosion (e.g., 12% failure in streetlights @3yrs).
Solid Aluminum:
Dielectric Aging: Organic insulation degrades under prolonged heat.
Why:
"湿气渗透" ➔ "Moisture Ingress" (engineering term).
Real-world data ("路灯项目3年故障率12%") contextualized for global audience.
5. Economics & Applications
Why:
"禁用" strengthened to "contraindicated" (medical term repurposed for technical severity).
"外接驱动板" ➔ "external driver" (industry-standard).



